Why Understanding Home Insurance Costs Matters for New England Homeowners
The average home insurance cost in the U.S. is about $2,424 per year for a policy with $300,000 in dwelling coverage. However, premiums in New England are unique.
- Massachusetts homeowners pay an average of $1,595 to $2,132 per year.
- New Hampshire homeowners pay an average of $1,039 to $1,658 per year.
Rates are rising nationwide due to inflation, higher building costs, and severe weather. Understanding what drives your premium is the first step to controlling it. Your home is your biggest investment, and the cost to protect it shouldn’t be a mystery.
As Geoff Stanton, President of Stanton Insurance Agency, I’ve helped countless Massachusetts and New Hampshire homeowners steer the average home insurance cost and find coverage that fits their needs. With decades of local experience, I understand the factors that make our region unique—from coastal storm risks to the impact of harsh New England winters.
What is the Average Home Insurance Cost?
When shopping for home insurance, the first question is always about cost. The average home insurance cost in the United States is approximately $2,424 per year, or about $202 per month, for a policy with $300,000 in dwelling coverage. However, this national average is just a starting point. Your actual premium depends on your specific circumstances, from your home’s location and age to your personal claims history and coverage choices.
Most homeowners pay premiums monthly or annually. While monthly payments can feel more manageable, paying annually often comes with a discount, as insurers may charge a small service fee for processing recurring payments. If you have a mortgage, your lender likely requires your premium to be collected through an escrow account, which is automatically included in your monthly mortgage payment.
Premiums vary dramatically across the country due to risk. States facing frequent natural disasters like hurricanes, wildfires, or tornadoes have much higher rates. If you’ve been wondering why is my home insurance so expensive?, rising construction costs are a major factor. The increasing cost of lumber, labor, and other materials makes it more expensive for insurers to rebuild homes, and that cost is passed on to policyholders.
Average Home Insurance Costs in Massachusetts and New Hampshire
For those of us in Massachusetts and New Hampshire, local numbers are what matter. The good news is that both states tend to have rates below the national average.
| Location | Average Annual Cost (for $300k Dwelling Coverage) | Average Monthly Cost (for $300k Dwelling Coverage) |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. National Average | $2,424 | $202 |
| Massachusetts | $1,595 – $2,132 | $133 – $178 |
| New Hampshire | $1,039 – $1,658 | $87 – $138 |
Data compiled from multiple industry sources for $300,000 in dwelling coverage.
The average home insurance cost in Massachusetts ranges from $1,595 to $2,132 annually, while New Hampshire homeowners often see lower rates, averaging between $1,039 and $1,658 per year. For a deeper dive into coverage options specific to our state, check out our guide to MA Homeowner Insurance.
Why Costs Vary So Much by Location
Even if you and your neighbor have identical homes, your premiums might differ. Insurers analyze risks associated with your specific location, sometimes down to the ZIP code.
Proximity to the coast is a major factor in New England. Homes along the shoreline face higher risks from Nor’easters and hurricanes, leading to higher premiums. Winter storm risk also affects rates, with areas prone to ice dams and heavy snow seeing increases. Insurers also review local crime rates using data from sources like the FBI Uniform Crime Report to assess the risk of theft. Your proximity to a fire department and hydrants can lower your costs, as faster response times reduce potential damage. Finally, local rebuilding costs play a key role; if labor and materials are expensive in your area, your premium will be higher to reflect the true cost of rebuilding.
Key Factors That Determine Your Home Insurance Premium
Insurers use dozens of data points to calculate your rate. Understanding what goes into your average home insurance cost allows you to make informed decisions and potentially save money.
Your Home’s Characteristics
The physical attributes of your property play a huge role in determining your premium, as they indicate how much it would cost to rebuild and how likely it is to suffer damage.

- Dwelling Coverage Amount: This is the single biggest factor. It’s the amount needed to rebuild your home’s structure. A common mistake is confusing market value (what your home sells for) with replacement cost (the cost to rebuild). Always insure for replacement cost. Learn more about how dwelling coverage affects cost.
- Home’s Age: Older homes are often more expensive to insure because of degraded materials and outdated systems that don’t meet modern building codes.
- Construction Materials: Homes built with fire-resistant materials like brick generally have lower rates than wood-frame homes.
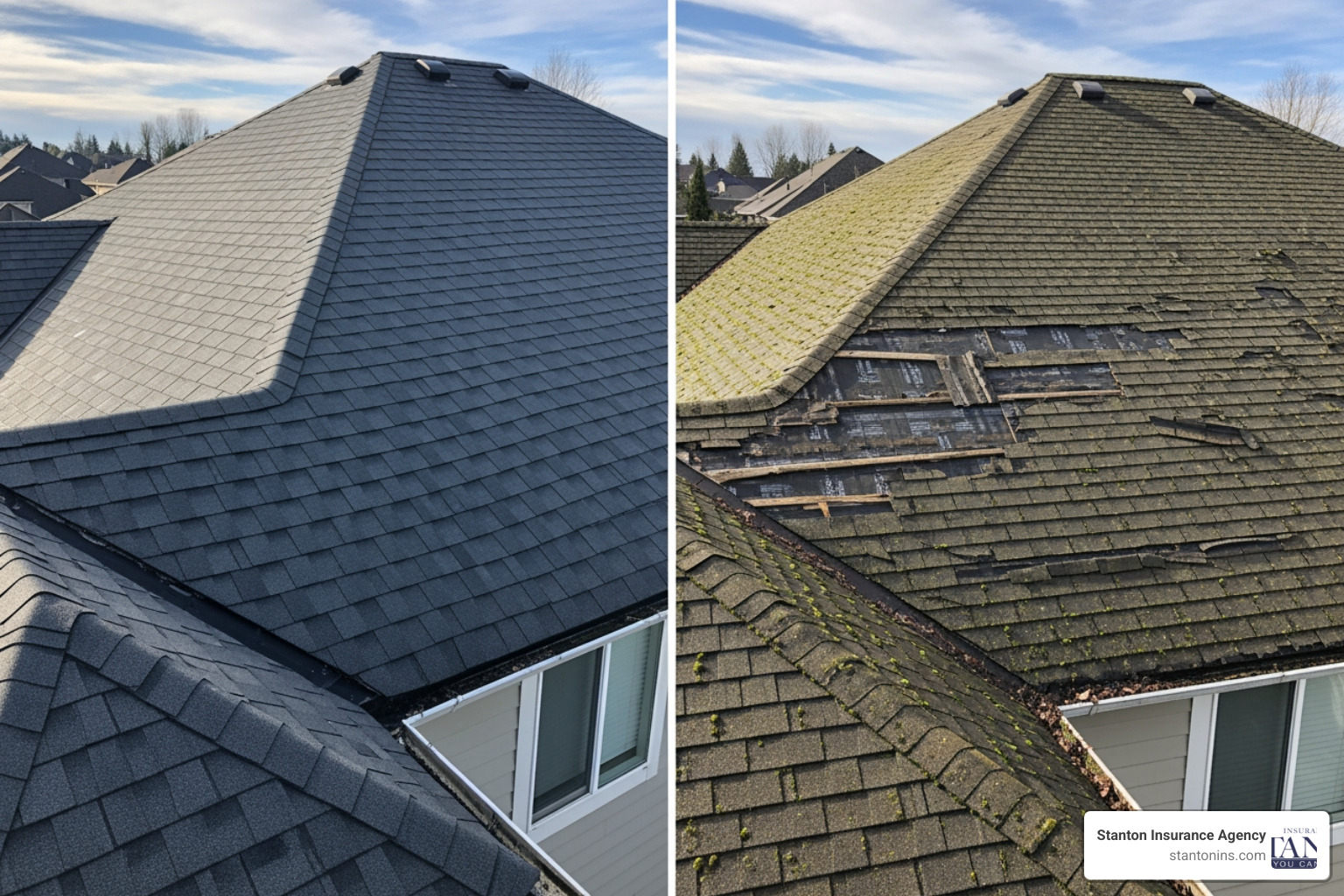
- Roof Type and Age: A new roof made with durable materials can lead to lower premiums. An old roof (over 20 years) will increase your rates, and some insurers may even require replacement before issuing a policy.
- Electrical and Plumbing Systems: Updated systems reduce the risk of fire and water damage, which can translate to lower premiums.
Your Personal Profile and History
Your personal history also contributes to your premium calculation.
- Credit-Based Insurance Score: In Massachusetts and New Hampshire, insurers use a score derived from your credit report to predict the likelihood of a claim. Homeowners with poor credit may pay up to 137% more than those with excellent credit. Understanding how credit affects insurance rates can help you improve your score.
- Claims History: Insurers review the past five to seven years of claims. Multiple claims, even small ones, can signal higher risk and lead to increased rates. This is why it’s often wise to pay for minor repairs out of pocket rather than filing a claim.
- Marital Status: Some insurers offer small discounts to married couples, as data suggests they tend to file fewer claims.
Property Risks and Coverage Choices
Certain property features and your coverage choices also impact your premium.
- Attractive Nuisances: Features like swimming pools and trampolines increase liability risk and your premium. Insurers may require safety features like fencing.
- Certain Dog Breeds: Some breeds deemed “high-risk” can lead to higher liability premiums or even denial of coverage for dog-related incidents.
- Home-Based Business: A standard policy doesn’t cover business liabilities. You’ll need a separate policy or an endorsement, which will increase your cost.
- Deductible Amount: You have direct control here. A higher deductible means a lower premium. Raising your deductible from $1,000 to $2,500 could reduce your premium by about 12%. When choosing a deductible, ensure you can afford the out-of-pocket cost.
- Liability Coverage Limits: Higher limits provide more protection and will increase your premium, but the cost is often modest for the significant extra protection you receive.
Practical Strategies to Lower Your Home Insurance Bill
While some cost factors are fixed, you have more control than you might think. Proactive steps can lead to significant savings on your annual premium.
Discounts and Policy Adjustments
We’ve helped countless homeowners in Massachusetts and New Hampshire find savings they didn’t know existed. Here are the most effective ways to reduce your average home insurance cost.
- Bundle your home and auto insurance: This is one of the simplest strategies. Most insurers offer a multi-policy discount that can range from 5% to 25%.
- Raise your deductible: Increasing your deductible from $1,000 to $2,500 could reduce your annual premium by about 12%. Just be sure you have an emergency fund to cover the higher amount.
- Stay claims-free: Insurers often provide discounts after you’ve gone several years without a claim. Think twice before filing small claims you could pay for out of pocket.
- Ask about loyalty discounts: Some companies reward long-term customers. However, it’s still wise to review your coverage annually to ensure you’re getting competitive rates.
- Pay your premium in full: Many insurers offer a discount for paying annually, and you’ll avoid monthly administrative fees.
For more detailed strategies, explore our guide: Saving on Home Insurance: Practical Strategies for Homeowners.
Home Safety and Mitigation Upgrades
Investing in your home’s safety can put money back in your pocket through lower insurance premiums.
- Security systems: Monitored burglar alarms, deadbolts, and cameras can deter theft and earn you a discount.
- Fire prevention measures: Interconnected smoke detectors are a must, but a fire sprinkler system can lead to substantial premium reductions.
- Water leak sensors: These smart devices detect leaks early, preventing costly water damage claims. This is especially relevant for preventing Winter Home Insurance Claims from frozen pipes.
- Storm shutters: For coastal homeowners, these can prevent thousands in wind damage and often qualify for a discount.
- Upgrade your roof: A new, impact-resistant roof is one of the most impactful improvements you can make, often leading to significant premium reductions.
Decoding Your Policy: What’s Covered and What’s Not
Your homeowners insurance policy is a comprehensive safety net, but it has specific limits. Understanding what is and isn’t covered is essential to ensuring you’re truly protected.
Standard Homeowners Insurance Coverage
A typical policy (usually an HO-3 form) is divided into several sections, each protecting a different aspect of your life.
- Dwelling coverage (Coverage A): This is the foundation, covering repairs or rebuilding of your home’s physical structure if damaged by a covered event.
- Other structures coverage (Coverage B): This protects structures not attached to your home, like detached garages, sheds, and fences. It’s typically 10% of your dwelling coverage.
- Personal property coverage (Coverage C): This protects your belongings, from furniture to electronics. You can choose between actual cash value (pays depreciated value) or replacement cost (pays for new items). Replacement cost offers better protection.
- Loss of use coverage (Coverage D): Also called Additional Living Expenses, this pays for hotel stays and other costs if your home becomes uninhabitable after a covered loss.
- Personal liability coverage: This protects you if someone is injured on your property or if you damage someone else’s property, covering legal fees and settlements.
- Medical payments coverage: This is a smaller, no-fault coverage for minor medical expenses if a guest is injured on your property.
For those curious about other property types, you can explore What does condo insurance cover?, which has key differences from a standard home policy.
Common Exclusions and Optional Add-ons
Standard homeowners insurance doesn’t cover everything. Some of the most significant risks are excluded.
- Flooding: Damage from floods, storm surge, and overflowing rivers is NOT covered. You need a separate policy, typically through the National Flood Insurance Program or a private insurer. To learn more, read our guide on Why is Flood Insurance Important?.
- Earth Movement: Earthquakes, sinkholes, and landslides are typically excluded.
- Pest Damage: Termites, rodents, and other pests are considered a maintenance issue, and the damage they cause is not covered.
- Wear and Tear: Insurance covers sudden, accidental events, not gradual deterioration from age or neglect.
- Water Backup: Damage from backed-up sewers or drains is usually excluded, but you can often add this coverage with an endorsement for a small additional premium.
To bridge these gaps, you can add endorsements (or riders) for things like extended dwelling coverage, scheduled personal property for valuables, and identity theft protection. Each adds to your average home insurance cost but provides valuable peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions about Home Insurance Costs
Here are straightforward answers to the most common questions Massachusetts and New Hampshire homeowners ask about their insurance bills.
Why are home insurance rates increasing?
If you’ve noticed your premium climbing, you’re not alone. The average home insurance cost is rising for two main reasons. First, inflation has driven up the cost of building materials and labor, making home repairs and rebuilding far more expensive. Second, we’re seeing more frequent and severe weather events. According to the Insurance Information Institute, these trends have forced carriers to adjust rates to cover the increased risk and cost of claims.
What is the 80% rule in homeowners insurance?
The 80% rule is a guideline used by insurers to ensure you carry adequate dwelling coverage. It states that your policy must cover at least 80% of your home’s total replacement cost. If you’re insured for less and suffer a partial loss (like a kitchen fire), your insurer may only pay a portion of your claim, leaving you to cover the rest. The best practice is to insure your home for 100% of its replacement cost, not its market value, to avoid any penalties and ensure you’re fully protected.
How does condo insurance cost compare to home insurance?
Condo insurance (HO-6) is typically much cheaper than a standard homeowners policy, often less than half the cost. This is because your condo policy only needs to cover the interior of your unit (“walls-in”), your personal belongings, and your liability. The condo association’s master policy covers the building’s exterior, roof, and common areas, with the cost shared among all unit owners through HOA fees. This significantly reduces your individual insurance burden.
Find the Right Coverage for Your New England Home
Understanding the average home insurance cost is about knowing what you’re paying for and ensuring your money is protecting your biggest investment. Your home’s insurance should reflect your unique situation, from its location to its construction.
We’ve shown you how premiums are calculated, why costs vary across New England, and how factors like your roof’s age and deductible choice impact your bill. We’ve also covered practical ways to lower your premium, from bundling policies to installing safety devices.
Every home is different. A new colonial in Needham, MA has different risks than an older home in rural New Hampshire. That’s why working with a professional who understands the local market is so valuable. As a local, independent insurance agency, Stanton Insurance Agency has deep roots in Massachusetts and New Hampshire. We understand our region’s unique challenges, from Nor’easters to ice dams, and know how to help you steer them.
Our goal is to find the right balance between comprehensive protection and a premium that fits your budget. We’ll review your coverage, identify potential gaps, and find every available discount.
Whether you’re a first-time homeowner or frustrated by rising rates, we’re ready to help. For a policy customized to your home, get a personalized Home Insurance Quote today.

